Learn More About Overnight Summer Camp
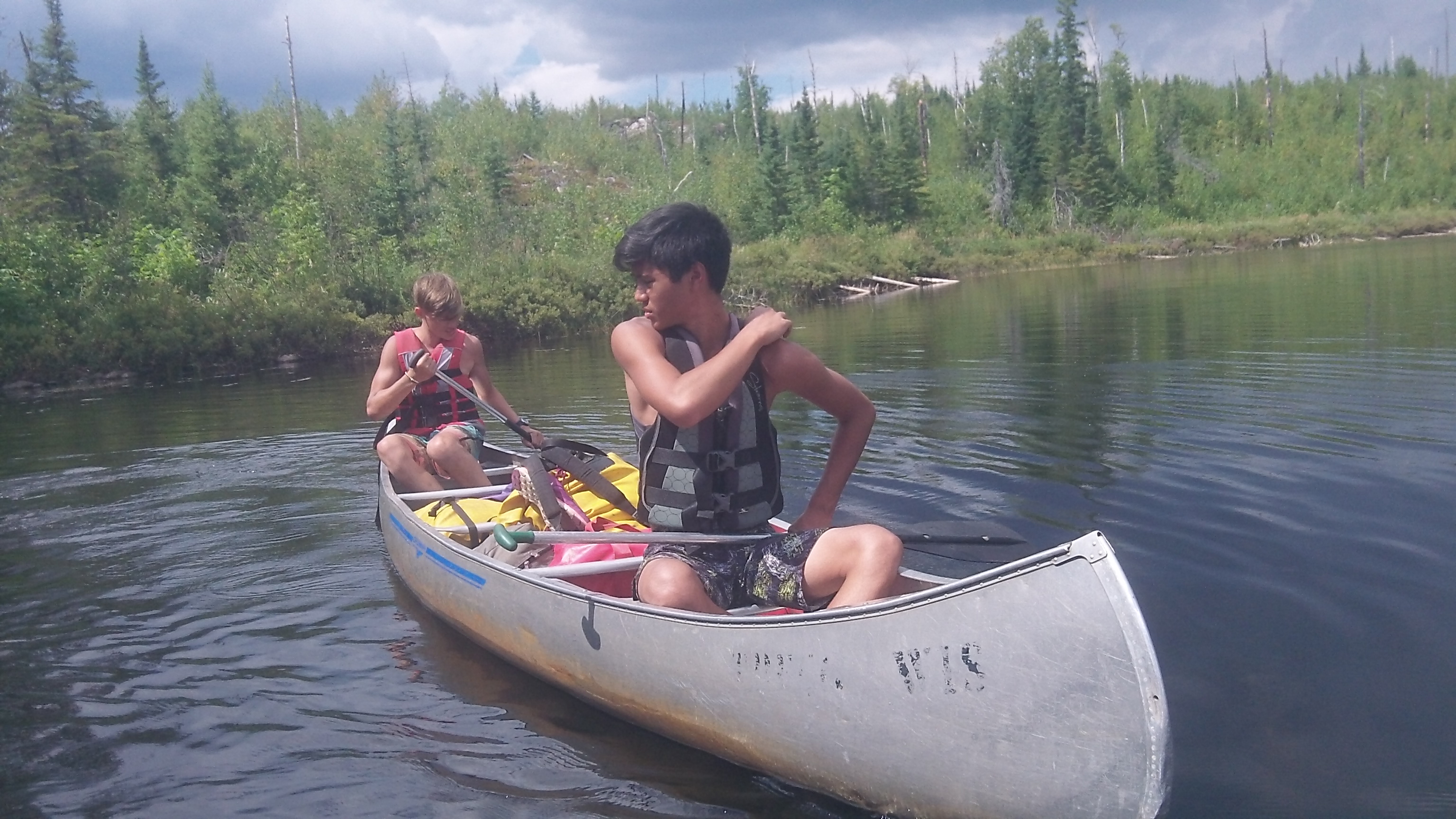



Here are 3 Must Do's before you send your child off to the Northwoods of Minnesota:
1) Scour The Website
Every camp has a website. Yet, not all websites are created the same, be sure to look past the smiling campers faces. What is the feel of the site? Was it created by a camp director or was it built by a professional company that puts all the latest bells and whistles on the site to impress you and your child. Next, does the site have the information? Read, read, read, This day and age we all want to do things fast and get them done, but remember, you are sending your most important asset out alone to an overnight summer camp in Minnesota. For instance, at Swift Nature Camp they have a parent section with a section "Policies that Protect Campers" . Having a section like this helps show that they are dedicated to child safety, even the things that are so bad nobody want to talk about them. Remember this, any summer camp can create a website, and all websites are advertising, they are not going to tell you the bad stuff that happened at camp last year, so it is important to know who stands behind the site and the summer camp you are sending your child off too.
2) Talk To The Camp Director
Every camp has a leader. This position sets the tone for staff development, camper and parent interactions and camp safety. For many camps this is a part time position and often given to a person who is still in their 20's with little experience. I once called a camp in Minnesota and they told me that I could not speak to a camp director because they don't do that. When I inquired why, they mentioned they did not have an overnight summer camp Director yet. By calling the camp directors you have the opportunity to ask questions about the philosophy and feel of the camp. Do you feel the Director understands children and knows how to manage a staff of 18-22 year old staff members. The camp director is the most important person at your summer camp be sure you chat with them and have your questions ready in advance. SummerCampAdvice has a worksheet to help pick the right camp .
3) Ask For References
References are the key to knowing that the overnight summer camp you pick is the right one for your child. As parents, talking to references will help give you some insight into what another parent thinks about the camp. The best way to do this is call the camp director and ask for at least 3 references. This will help prove that the camp has relationships with its families and is not just processing children through its program. Questions to ask the parents might include: Was your child homesick? What did the camp do to help? or Why did you select this camp? Don't forget that talking to references can be children as well. So talking to the camper has great insight. Some questions might include: What was your happiest time? Why? Did you ever feel scared? Your child might even put together a few questions they feel are important and then they can ask them of the camper. Talking is important dont text, dialog is important and the tone of the conversation can give you even more information. Remember this is a fact gathering task so be open
Overnight summer camps in Minnesota have a very good safety record, better than public schools in Minnesota. As parents, we want more than our kids being safe at camp. We want our child to benefit from all that camp provides. We know that summer camp provides a place for kids to learn to swim, sleep in a cabin and sing around a campfire, they can be rewarded with personal development skills that can help them in the classroom, in their relationships and in whatever calling they choose. At our camp we often talk about the Magic of summer camp and when I ask campers and staff what this means the answer that I most often get is "Swift Nature Camp creates a place where I am my BEST Self" and isn't that the best thing we as parents want for our children summer camp experience?
Swift Nature Camp is an overnight nature camp for boys and girls ages 6-15. Our focus is to blend traditional summer camp activities while increasing a child's appreciation for nature, science and the environment. Swift Nature Camp offers traditional summer camp activities along with an environmental focus. Campers enjoy an active Nature Center, Pet Zoo, and Department of Natural Resources sponsored programs, plus recreational activities that include canoe and backpack trips, horseback riding, swimming, arts & crafts, team courses, archery, sailing, water skiing, tubing and sports.
Our special Discovery Camp is a nurturing program for first-time overnight campers, offering additional staff to provide support and encouragement to overcome homesickness and build confidence. The program welcomes no more than 50 first-time campers, and the special attention that this intimate group receives is the reason that more than 92% of them wish to return.
 Jestem dyrektorem obozu letniego dla dzieci i młodzieży ale przede wszystkim jestem rodzicem. Obserwując zjawisko spędzania wielu godzin przez nasze dzieci przed ekranem komputera lub telewizora ogarnia mnie przerażenie. Co się stało, że najmłodsi zamienili zabawę na świeżym powietrzu na długotrwałe przesiadywanie w zamkniętym pomieszczeniu przez elektronicznym urządzeniem? Jeszcze nie tak dawno, pamiętamy to ze swojego dzieciństwa, kiedy dzieci miały wolny czas, beztrosko bawiły się z rówieśnikami, czytały książki, goniły po podwórku i sąsiedztwie. Dziś wybierają ekran komputera, tabletu czy telefonu. To nowy styl życia, który przejęła nie tylko młodzież. Dochodzi do takich paradoksów kiedy rodzice karząc dziecko zobowiązują go by wyszło z domu. Dla nas karą było gdy rodzice zabronili nam wyjść do kolegów na podwórko. Często my dorośli nie tylko nie sprzeciwiamy się takim sytuacjom ale sami promujemy taka formę wypoczynku. Być może czasem zwrócimy naszym dzieciom uwagę by odłożyły komputer, czy telefon ale tak naprawdę nie wiele to daje. To od nas, jako rodziców, zależy czy dzieci zachowają zdrowe proporcje bycia " na internecie" i " poza internetem".
Jestem dyrektorem obozu letniego dla dzieci i młodzieży ale przede wszystkim jestem rodzicem. Obserwując zjawisko spędzania wielu godzin przez nasze dzieci przed ekranem komputera lub telewizora ogarnia mnie przerażenie. Co się stało, że najmłodsi zamienili zabawę na świeżym powietrzu na długotrwałe przesiadywanie w zamkniętym pomieszczeniu przez elektronicznym urządzeniem? Jeszcze nie tak dawno, pamiętamy to ze swojego dzieciństwa, kiedy dzieci miały wolny czas, beztrosko bawiły się z rówieśnikami, czytały książki, goniły po podwórku i sąsiedztwie. Dziś wybierają ekran komputera, tabletu czy telefonu. To nowy styl życia, który przejęła nie tylko młodzież. Dochodzi do takich paradoksów kiedy rodzice karząc dziecko zobowiązują go by wyszło z domu. Dla nas karą było gdy rodzice zabronili nam wyjść do kolegów na podwórko. Często my dorośli nie tylko nie sprzeciwiamy się takim sytuacjom ale sami promujemy taka formę wypoczynku. Być może czasem zwrócimy naszym dzieciom uwagę by odłożyły komputer, czy telefon ale tak naprawdę nie wiele to daje. To od nas, jako rodziców, zależy czy dzieci zachowają zdrowe proporcje bycia " na internecie" i " poza internetem".
Ile czasu twoje dziecko spędza przed ekranem? Dwie godziny, trzy, pięć...? Ostanie badania naukowe wykazały, że dzieci i młodzież w wieku 8-18 lat spędzają przeciętnie 7.5 godziny dziennie przed ekranem. Co w tym takiego złego? Efektem takiego stylu życia sa problemy z koncentracja uwagi, problemy wychowawcze, trudności w nauce, w zasypianiu, otyłość czy powolny zanik tradycyjnych relacji międzyludzkich. Lekarze opisują nową etiologię nadciśnienia tętniczego u nastolatków, która wynika z wielogodzinnych sesji “online” spędzonych na grach komputerowych. Młodym ludziom coraz trudniej nawiązywać kontakty " twarzą w twarz". Ekran to rozrywka i często dla tzw. świetego spokoju pozwalamy dzieciom na taka formę zabawy. Przyjrzyjmy sie sytuacjom codziennym np. w restauracji. Nie rzadko siedząca przy stole rodzina podzielona jest na tych, którzy rozmawiają patrząc sobie w oczy( to zwykle starsze osoby) i tych, którzy wpatrzeni sa w ekran telefonu i nie sa zaangażowani w rodzinna rozmowę. Jeśli chcemy zmiany, wszyscy musimy podjąć w tym celu odpowiedni wysiłek.
Zarówno my rodzice jak i dzieci powinniśmy ograniczyć czas spędzany przed ekranem. Nie możemy mieć wymówki, ze był ciężki dzień w pracy dlatego siadamy przed telewizorem i sie relaksujemy. Jako rodzina usiądźmy razem i porozmawiajmy o tym nowym stylu życia.
1) Ustalmy reguły według których wiadomo będzie ile czasu przed ekranem jest dopuszczalne.
W naszym domu jest to przywilej, nagroda za odrobione lekcje i wykonanie innych obowiązków.
2) Tak jak jest zakaz prowadzenia pojazdów i tekstowania, wprowadźmy podobne zasady w domu. Np. Zakaz tekstowania przy stole w czasie posiłku, czy po określonej godzinie.
3) Dzieci często uciekają sie do ekranu bo nie wiedza co z sobą zrobić. Zachęćmy je do zabaw z naszego dzieciństwa, niech pogonią po podwórku, łapią żaby, robią łuki z patyków a jak zimno na zewnątrz niech budują z LEGO, rysują, układają puzzle. A jak jest możliwość to i my zaangażujmy sie w rodzinny spacer, czy wycieczkę rowerową.
W naszym domu tradycją stał sie wieczór gier planszowych, na które często wparszaja sie znajomi. Czas spędzony przed ekranem jest ograniczony do 30 minut po wykonanych obowiązkach. Raz w tygodniu mamy wieczor kiedy zasiadamy jako rodzina i oglądamy film odpowiedni dla nas wszystkich. Czy taki styl życia jest łatwy? Zdecydowanie nie, to nasz wybór. Ale za to możemy więcej czasu spędzić razem i wcale to nie jest takie złe :)
Niech to będzie wyzwanie dla całej rodziny. Walczmy z tym technologicznym potworem i nie dajmy sie mu pożreć. Postęp technologiczny jest wspaniały i ważne jest by dzieci potrafiły z niego korzystać, jednak nie pozwalajmy by przez to zanikały międzyludzkie relacje czy tradycyjne wartości.
Pozdrawiam serdecznie,
Jola Lorenz
Wlasciciel obozu Swift Nature Camp
www.SwiftNatureCamp.com
Summer Camp is Expensive
As parents we often make decisions that are hard. Yet, we know these decisions are the best for our children. Summer Camp is no exception. We know deep down that camp will help our Childs independence, empathy and team building skills Yet, camp is expensive. So you want to save money on summer camp? Who doesn't! The best way to save money on Summer camp is to start looking as soon as possible. Here is a quick list of just a few of the ways to save on your Childs overnight camp experience.
1. Summer Camp Special Offer
Many camps may have special offers. It will take research to find them. Some camps will even reduce prices if they need to fill beds at a particular session. So having flexibility in dates and talking with the camp director you may be able to save. Right now Swift Nature Camp is having A First timer Summer Camp special offer saving nearly 30% off the session price.
Many camps have camper ships that allow families in need to reduce the price of camp. At Swift Nature Camp we believe that every child should go to camp so we offer financial assistance programs. We look for donations plus we match our donations but these are on a first-come, first-served basis so funds do run out.
Yes, Even if you don't qualify for scholarships or other discounts, you may be able to pay for day camp for kids under 13 using pre-tax dollars in a dependent care flexible spending arrangement (FSA). The IRS caps dependent care FSAs at $5,000 per year, and your employer withholds money from each paycheck to fund the plan.Also consider the Child and Dependent Care Credit, which allows taxpayers to deduct up to 35 percent of their childcare expenses, up to a maximum of $6,000. The best advice is to check with a tax planning professional and keep track of expenses and check the latest tax code.
4. Register Early.
Many summer programs reward the early bird. So shop in the fall for the upcoming summer. Before registering ask if the camp provides any early bird pricing. You will be surprised.
“The memories of camp far outlast the price of camp”. This saying is very true children that attend camp will have positive memories for a lifetime. Yes, prices should play an important role in your decision, but it should not the only factor when selecting where to send your child.
Parents need to realize that a quality overnight summer camp is so much more than just daycare. An intentional camp wit provide your child with: responsibility, compassion, cooperation, trying new things and independence just to name a few. The American Camp Associations have been doing studies for years that show the positive effects of summer camp.
In a recent article "Five Childhood Experiences That Lead to a More Purposeful Life"it was suggested that children that experience conflict and adversity in a positive setting can ultimately create more purposeful life. When we send our children off to camp it can be hard for many children and yet that experience is good for them. As parents we often need to think past today and what the long term impact for our child might be. The right camp will have a positive effect.
To learn more about picking the right summer camp see SumerCampAdvice.com


Here are a just a few of the more important questions:
- How long are the sessions?
- How are staff trained?
- Is an RN or Doctor on staff?
- Are activities going to be enjoyed by your child?
- Coed or single gender?
- How many children, How many staff?
- Are cell phones allowed?
- What is the cost?
- Is the camp Accredited by the American Camp Association?
To find a detailed list of questions to answer please see Summer Camp Advice.
The above list is only a beginning of question needed. So you can see that when you get to the point of thinking about location many other areas of concern should have already been addressed. Parents need to realize they need to trust the camp and its directors in order to achieve some of the benefit of an overnight camp. This is why it is important for parent to contact the directors and create a personal relationship with the camp.
- Here are a few Reasons to choose a camp farther from home:
It's worth it: There may be something about a camp that makes the travel worth it. If your child wants to specialize in sailing or mountain climbing, you'll need to choose a camp that meets those need. A parent may have a preference for a camp that they once attended, even if they no longer reside in the area. -
Diversity: While your camper may not see as many familiar faces in a camp far from home, this may be just what he or she, and you, want. Children may want to separate their camp life from the lives they lead the rest of the year, having the opportunity to begin the program with a 'clean slate'. Campers often have a sense of freedom when they go to a camp where they don't know anyone.
-
The distance doesn't bother the camper or parents: Many children find traveling alone, even by airplane, exciting rather than scary. Assuming that proper travel arrangements are made, you may be comfortable with a camp away from home.
- So when picking a sleep away summer camp do your homework. Realize that many many considerations need to be made and and be aware that overnight camps near me should not be your first search term. Using this, you will limit your options and minimize many of the benefits summer camp can provide.
Jeff and Lonnie Lorenz, directors of Wisconsin’s Swift Nature Camp for twenty five years, believe summer camp is a unique opportunity for dimensional childcare at the best value. A sleep away summer camp experience will benefit each child by creating memories, try new things, gain skills and independence and make new and lifelong friends. Summer camp is more than child care it is an opportunity for personal growth. The First Time Camper program is the perfect place to start on an overnight summer camp adventure.
 Summer camp is a special place it give children a place to call home that is less structured has less pressure than their home routines of school and sports. Plus it gives kids a chance to experience life in a screen free zone, just like the olden days. Yet when an overnight summer camp has an environmental Education focus, camp doubles up its value to campers and parents alike.
Summer camp is a special place it give children a place to call home that is less structured has less pressure than their home routines of school and sports. Plus it gives kids a chance to experience life in a screen free zone, just like the olden days. Yet when an overnight summer camp has an environmental Education focus, camp doubles up its value to campers and parents alike.
At Swift Nature Camp is an environmental education summer camp in Wisconsin that is rooted in fun with nearly 50 different land and water activities its hard not to have fun. Learning new skills in a non competitive fun way allows each child to participate at their level and try to better themselves. To give children autonomy, camp daily gives children the opportunity to select the activities that they want to do that day. So in a way a camper get to create their own camp experience rather than having adults give them a schedule. Kind of like the old days when chidden could just go outside and play.
Our campers love nature and environmental studies, so at Swift Nature Camp we blend camp activities with outdoor education along with summer fun. Our goal is to have our campers uses an exploration to developing an hands on appreciation and understanding of the natural world in Wisconsin that is right outside their cabin door. .Our interactive activities utilize scientific skills of discovery, observation and investigation. Yet what are campers love is our Nature Center and Camp zoo. Here many native animals are kept as well as other small pets. Campers even have the opportunity to adopt an animal while they are at camp. These critters are for learning responsibilities and animal care.
Our daily environmental classes seeks to teach campers about human impact on the environment and to be aware of how they are connected to nature. This individual responsibility is the key to teaching children about conservation. our hydroponic garden project is special because the campers help catch the fish that help verbalize the plants living in the garden, this interaction helps make the concepts stick. SNC
Not only do campers learn Environmental Education but this overnight summer camp in Wisconsin let's children learn skills in personal relationship building. Kindness and understanding are the corner stone to cabin life, helping to insure team-building and cooperation. To learn more about Environmental Education in Wisconsin
Minnesota is blessed with many natural resouces and a rich natural back drop. Yet, Minnesota is becoming increasingly urban, not just Minneapolis or St Paul, so too is the percentage of Minnesotans living in Greater Minnesota’s cities and towns. In 2010 census, 73.3 percent of Minnesotans lived in urban areas.Yes, Minnesota life has changed! No longer are children exposed to nature as they used to be. Try this at home, ask a child 8-10 years old to describe an elephant or a bunny many will reach for a screen of some sort and want to show you. Yes, a picture is worth a 1000 words and yet something is lacking when we just reach for a screen.

I have asked many teachers over the years: "How is a Minnesota child's Environmental Science knowledge?" and most would say that the average child in Minnesota has less outdoor knowledge than thier grandparents. Some go as far as to say that some children have never touched a pine cone or picked up a worm on a rainy day. We have lost contact with the Environment. These same tachers say that they would love to teach more Environmental Education and take our kids outside, but they are so scheduled with what to teach that it gives them little opportunity.
Environmental Education Summer Camps are just one easy way a parent can empower their child's learning and reduce today's nature deficit. The urbanizatin of Minnesota reduces children's exposure to the the natural environment. It is more important than ever that our children get outside and reconect. Environmental education has numerous benefits, like helping children become good stewards and to think globally, as well as observe and act locally. Environmental education does more than just teaching about plants, animals and the world we live in. It is a valuable tool that encourages kids to think critically, observe nature and even sit quietly without a screen, all things we can use in our everyday world.
At Swift Nature Camp we take Environmental Education seriously, but not too seriously. Each day children will have the opportunity to be a part of our Nature Ceter activities. Many of the science activities are part of Nature Quest, the award-winning environmental program designed by the World Wildlife Federation,thus creating an amazing Environmental Camp. Our Nature Center and zoo at camp provide a dynamic setting for learning, as campers find themselves doing science experiments, conducting environmental testing, learning about the local wildlife, or participating in our camp recycling program. At Swift Nature Camp we even have a pond aquarium that campers can fill with their freshly caught turtles, frogs and fish. Our Nature's Neighbors live animal collection provides opportunities for up-close study and care of several common Northwoods residents, as well as a few exotic immigrants. Campers with their own small animals are encouraged to bring them to camp to share with others. The animals live in the Nature Center and camp Zoo, where all campers can enjoy and learn about them. As part of our environmental education campers can even adopt the pets while they are at camp, this gives a child responsibility while learning about their pet.
If you feel your child needs to get off their screen and be out in nature at a Minnesota Environmental Education Summer Camp then Swift Nature Camp is a wonderful place to make it happen. We even have an exclusive First Time at Camp program, perfect for the child who is new to spending the night away from home.
As parents we all want the best for our child. We have goals and want them to be thier best. Yet, thier is one thing that every parent MUST remember. Do you know what that is? Watch this video to learn this helpful 4 step program.